How to See System Uptime in Windows 10

If you wish to discover how long your PC has been powered on without a restart or a reboot, then all you need to do is see your Windows 10 uptime. With this uptime, one can monitor the previous restart status of your system. Uptime gives statistical data on the percentage of adequate operational time without a restart.

How to See System Uptime in Windows 10
Monitoring Windows 10 uptime will be helpful for some troubleshooting scenarios, and this article gives you a way to discover your Windows 10 uptime.
Method 1: Use Command Prompt
1. Type command prompt or cmd into Windows search then click on “Run as administrator“.
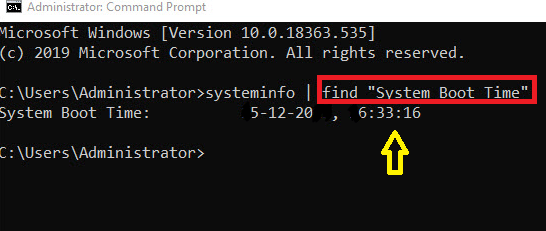
2. Now type the following command into cmd:
find “System Boot Time”
3. Once you have entered this command, hit Enter. In the following line, the Windows 10 uptime will be displayed as shown below.
Method 2: Use PowerShell
1. Launch PowerShell by searching for it using Windows search.
2. You can launch it by going to the Search Menu and typing Windows PowerShell then click on Run as administrator.
3. Feed the command in your PowerShell:
(get-date) – (gcim Win32_OperatingSystem).LastBootUpTime
4. Once your hit the Enter key, your Windows 10 uptime will be displayed as follows:
Days : 0 Hours : 14 Minutes : 45 Seconds : 51 Milliseconds : 974 Ticks : 531519745890 TotalDays : 0.615184891076389 TotalHours : 14.7644373858333 TotalMinutes : 885.86624315 TotalSeconds : 53151.974589 TotalMilliseconds : 53151974.589
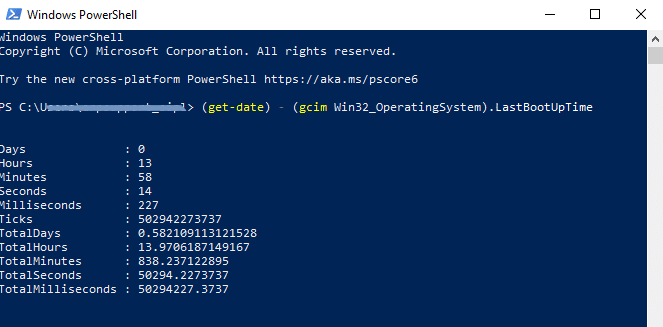
Using the second method, you can see several time details like uptime in days, hours, minutes, seconds, milliseconds, etc.
Also Read: What is the Difference between Reboot and Restart?
Method 3: Use the Task Manager
1. Open Task Manager by simply holding Ctrl + Esc + Shift keys together.
2. In the Task Manager window, switch to the Performance tab.
3. Select the CPU column.
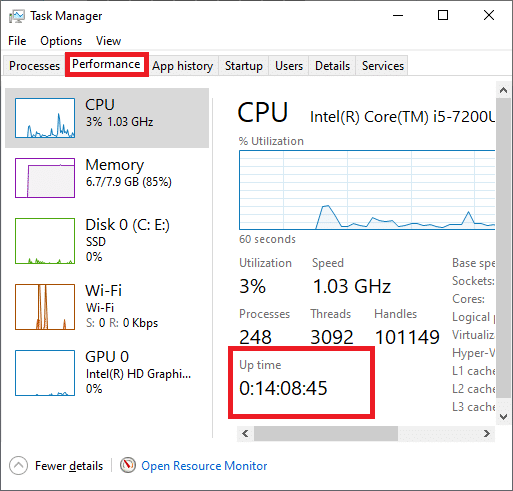
4. The Windows 10 uptime will be displayed as shown in the figure.
This method is quite an easier way to see system uptime in Windows 10, and since it gives graphical data, it is easy for analysis.
Method 4: Check Network Settings
When your system is connected to the internet using an Ethernet connection, you could use your network settings to monitor the Windows 10 uptime.
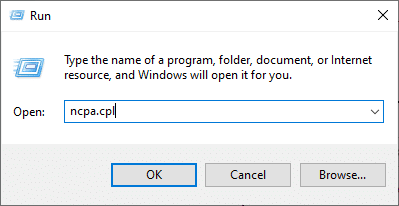
1. You can launch the Run dialog box by going to the search menu and typing Run.
3. Type ncpa.cpl as follows and click OK.
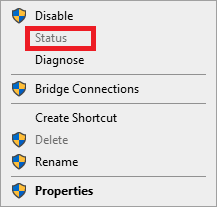
4. Right-click on the Ethernet network, you’ll see the Status option as follows. Click on it.
5. Once you click on the Status option, your Windows 10 uptime will be displayed on the screen under a name called Duration.
Method 5: Use the Windows Management Interface command
1. Launch the Command Prompt using administrative privileges.
2. Enter the following command into cmd and hit Enter:
wmic path Win32_OperatingSystem get LastBootUptime.
3. Your last boot-up time will be displayed as follows.
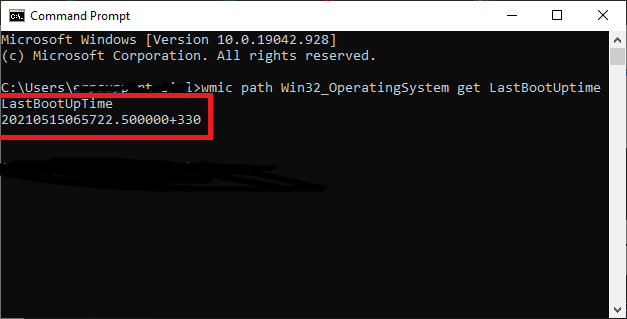
Some may want to find the uptime with a piece of numerical information as depicted above. It is explained below:
- Year of the Last Reboot: 2021.
- The month of the Last Reboot: May (05).
- Day of the Last Reboot: 15.
- Hour of the Last Reboot: 06.
- Minutes of the Last Reboot: 57.
- Seconds of the Last Reboot: 22.
- Milliseconds of the Last Reboot: 500000.
- GMT of the Last Reboot: +330 (5 hours ahead of GMT).
This means that your system was rebooted on 15th May 2021, at 6.57 PM, accurately at 22nd second. You could simply calculate your system’s uptime by subtracting the current operational time with this last rebooted time.
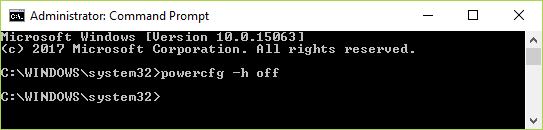
You cannot view your exact last boot uptime if your Windows 10 system has the Fast start-up feature enabled. This is a default feature provided by Windows 10. To view your precise uptime, disable this Fast start-up feature by running the following command:
powercfg -h off
Method 6: Use the Net Statistics Workstation command
1. You can launch the Command Prompt by going to the search menu and typing either command prompt or cmd.

2. You are advised to launch Command Prompt as an administrator.
3. Enter the following command and hit Enter:
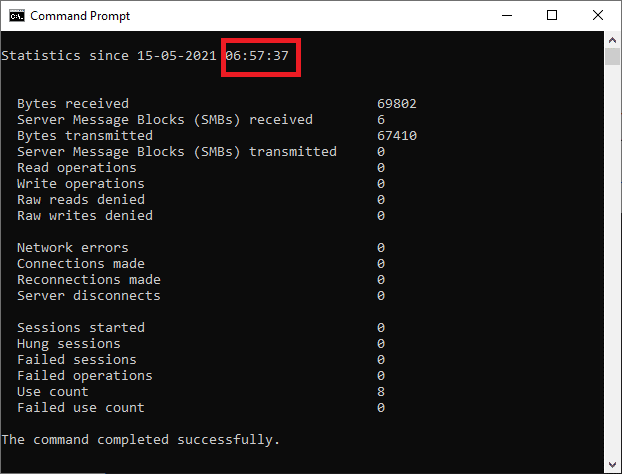
net statistics workstation.
4. Once you click Enter, you’ll see some data displayed on the screen, and your required Windows 10 uptime will be displayed at the top of the listed data as follows:
Method 7: Use the systeminfo command
1. Launch Command prompt using the above method.
2. Type the following command into cmd and hit Enter:
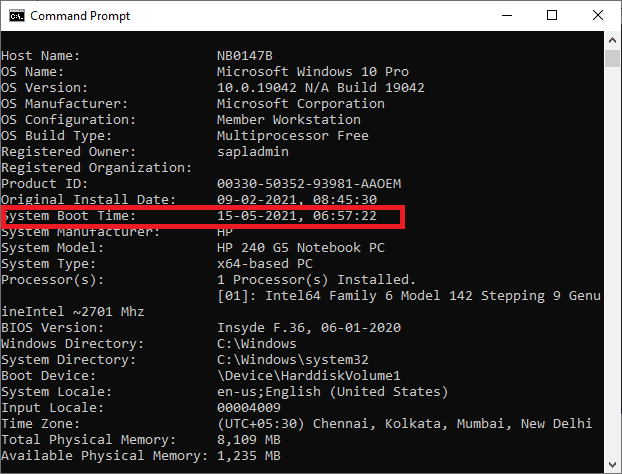
systeminfo
3. Once you hit Enter, you can see some data displayed on the screen, and your required Windows 10 uptime will be displayed along with the date you have performed during your last reboot.
All the above methods are easier to follow and they can be implemented not only for Windows 10 but also for other versions of Windows like Windows 8.1, Windows Vista, and Windows 7. The same commands are applicable in all versions.
Recommended:
We hope this article was helpful and you were able to see System Uptime in Windows 10. If you have any queries regarding this article, reach out to us through the comments section below.