- in windows 11 by Admin
What Is lsass.exe and Is It Safe?

Imagine a car with thousands of moving parts and looking under the hood to see all the parts whizzing and turning. Until one of them does something unexpected, it’s hard to know what to expect it to do. Yet you definitely know when something’s not right.
Some Windows processes are like that, and lsass.exe is one of them. When lsass.exe does its job, no one cares. When lssas.exe has high CPU usage or crashes, we notice and wonder why it’s even there.
What Is lsass.exe and Is It Safe?
All tools, in the wrong hands, are weapons. The lsass in lssas.exe is an acronym of Local Security Authorization Subsystem Service. Local Security Authorization is a system for authenticating users and logging them on. It also keeps track of security policies and generates system log alerts for events related to security.
You can imagine that when lsass.exe is doing its job, it’s a powerful tool and very safe. You can also imagine that when it’s not doing its job, things get bad.
How to Remove lsass.exe From Windows 11/10
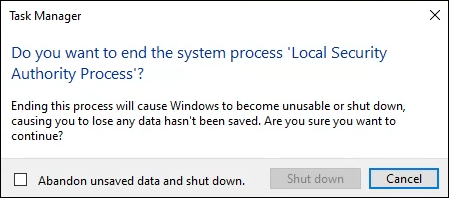
Don’t remove lsass.exe from Windows unless you’re certain it is a fake lsass.exe. It’s that crucial to Windows 11/10. Trying to kill the lsass.exe process in Windows 11/10 will result in the error message Do you want to end the system process ‘Local Security Authority Process’?
Choosing to do so will cause Windows to shut down and unsaved work will be lost. If lsass.exe fails for any reason, it will likely shut down Windows instantly.
How to Check If lsass.exe Is Real or Not
If you suspect that lsass.exe is causing issues, first check to see if it’s the real lsass.exe.
Check the lsass.exe Name Closely
The lower-case L, the upper-case i (I), and the number 1 can be deceptive to the eye. Hackers will substitute one for the other. What you think is the real lsass.exe could be Isass.exe or 1sass.exe.
The name of the fake process may also have a slight spelling variation. Perhaps there’s one S too many, a space, or some other small, easy-to-overlook difference.
Check Lsass.exe Digital Signature and File Location
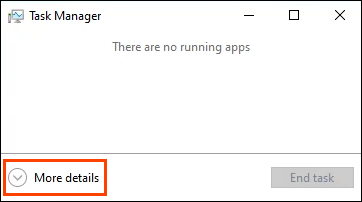
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager. Select More Details.
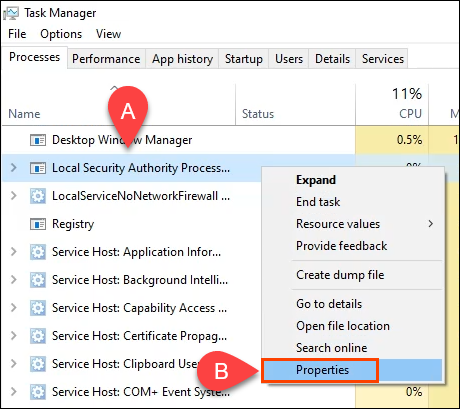
- Scroll down and find Local Security Authority Process. Right-click on it and select Properties.
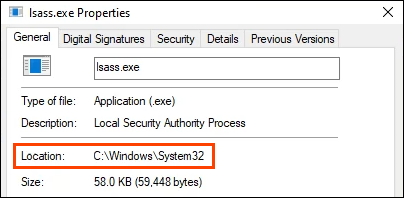
- On the General tab, next to Location it should read C:WindowsSystem32 or the equivalent for your system. Size should be very close to 58 KB. If it’s more than double that, you’ve probably got an issue.
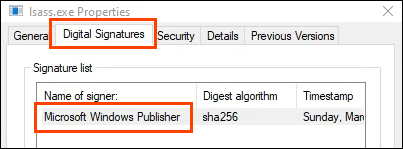
- On the Digital Signatures tab, the Name of signer should be Microsoft Windows Publisher.
Scan Lsass.exe With Microsoft Defender
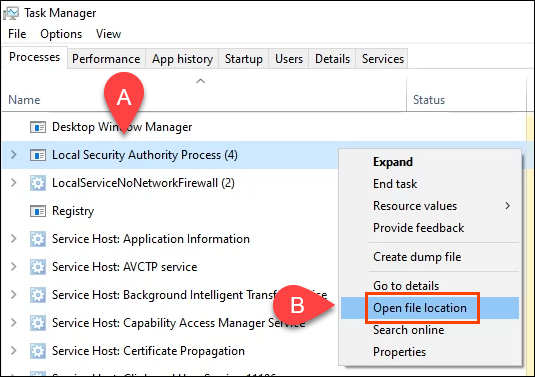
- In Task Manager, find Local Security Authority Process again. Right-click on it and select Open File Location.
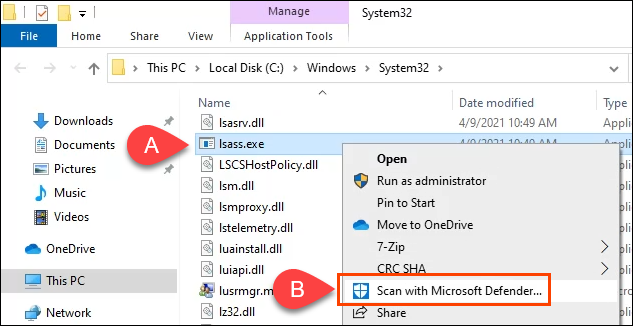
- File Explorer will open and lsass.exe will be selected. Right-click on it and select Scan with Microsoft Defender.
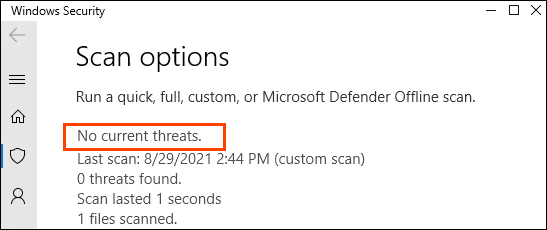
- The result should be No current threats.
If there are still concerns, do the same scan with a different trusted antivirus or antimalware application.
If any of the above checks fail, begin the process of removing viruses or malware from your computer.
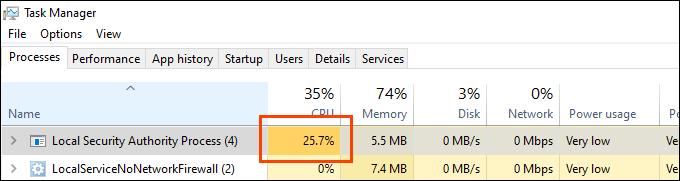
Can lsass.exe Cause High CPU, RAM, or Other High System Resource Usage?
Most critical Windows processes don’t use many resources. They have limited jobs and require little to carry them out. However, lsass.exe can spike when handling something like a login, yet it should return to using nearly nothing within a second or two.
If CPU usage by lsass.exe on a domain controller (DC) server is fairly high, it’s likely because it’s processing security for a large number of users. It controls the Active Directory database. If you know about Active Directory (AD), then it’s not surprising that lsass.exe will use more resources on a DC than on an average computer.
On a DC, expect lsass.exe to stay well under 10% CPU except for peak times of people logging on or off. On a PC, expect lsass.exe to stay under 1% most of the time.
If RAM or network usage by lsass.exe seems high, there’s a chance it’s not the real lsass.exe or it’s been infected. Take the usual precautions like running an offline virus scan with Microsoft Defender.
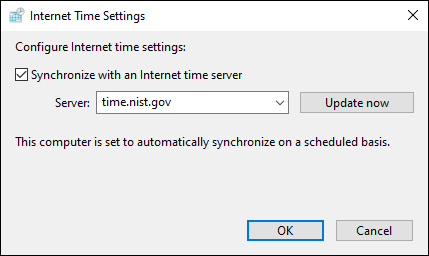
Anything that affects security can affect how many resources lsass.exe uses. Time differences between a DC and a system connected to it. Accurate time is crucial for things like security certificates. Check the DC and attached systems for time differences. You may want to use a Network Time Protocol (NTP) server to sync time for all devices on the domain.
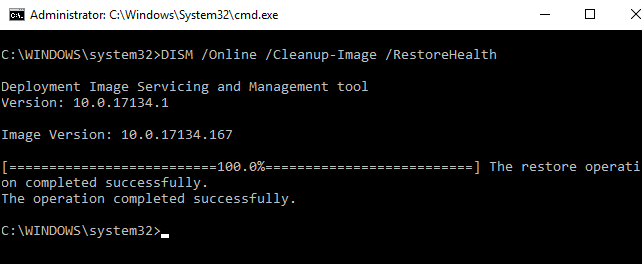
Corrupted system files may also be the cause of a legitimate lsass.exe’s high resource usage. Try using the SFC and DISM commands to clean up and repair system files.
If an offline virus scan and using the SFC and DISM commands don’t fix the problem, it’s possible the only option is to wipe and reinstall Windows.
Where Can I Learn More About Windows Processes?
Good on you for taking an interest in how your Windows device works! We’ve got many articles about Windows processes, whether they can be removed, and why the process may have CPU, memory, network, or disk usage that’s too high.
We also show how to use SysInternals Process Monitor and Process Explorer to troubleshoot issues. If you don’t see an article for the process you’re curious about, let us know. We’d be glad to write it for you.